UNTUK PEMESANAN HUBUNGI BIN MUHSIN
HP: 085227044550 Tlp: 021-91913103 SMS ONLY: 081213143797
@MyYM @MyFacebook @MyTwitter @MyYuwie @MyFriendster
binmuhsin_group@yahoo.co.id
===
Sedikit kondisi kesehatan yang disebabkan oleh faktor genetik saja. Some people may be prone to elevated cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity or type 2 diabetes. Beberapa orang mungkin rentan terhadap tinggi kolesterol, tekanan darah tinggi, obesitas atau diabetes tipe 2. But it's extremely uncommon that such health concerns are solely influenced by a familial predisposition. Tapi itu sangat jarang yang seperti itu adalah semata-mata masalah kesehatan dipengaruhi oleh kecenderungan keluarga. More often than not these conditions are influenced by diet and lifestyle choices that are less than optimal. Lebih sering daripada tidak kondisi ini dipengaruhi oleh pola makan dan pilihan gaya hidup yang kurang optimal. A pertinent analogy for this might be that genes are like a field. Sebuah analogi yang relevan untuk ini mungkin bahwa gen adalah seperti sebuah bidang. If you eat well, exercise regularly, practice stress reduction and supplement wisely, you will, in effect, encourage lush green plant life to grow. Jika Anda makan dengan baik, berolahraga secara teratur, praktek pengurangan stres dan suplemen dengan bijak, Anda akan, pada dasarnya, mendorong kehidupan tanaman hijau subur untuk tumbuh. However, if you don't take proper care of yourself, the field will become dry and lifeless. Namun, jika Anda tidak mengambil perawatan yang tepat dari diri sendiri, lapangan akan menjadi kering dan tak bernyawa. When ash or a spark comes drifting your way, which type of a field would you rather be? Ketika percikan abu atau datang hanyut cara Anda, jenis lapangan yang akan Anda suka?
On many occasions I've emphasized that supplements are not a replacement for healthy lifestyle choices. Pada banyak kesempatan saya sudah menekankan bahwa suplemen bukanlah pengganti pilihan gaya hidup sehat. But the fact of the matter is that many people fall short of their dietary and exercise goals. Tetapi faktanya adalah bahwa banyak orang jatuh pendek dari diet dan olahraga mereka tujuan. Another reality is that some people have stronger genetic hurdles to overcome. Kenyataan lain adalah bahwa beberapa orang memiliki genetik yang lebih kuat untuk mengatasi rintangan. In both of these instances, supplements can often play a more prominent role in managing wellness naturally. Dalam kedua kasus ini, suplemen dapat sering memainkan peran yang lebih menonjol dalam mengelola kesehatan secara alami.
According to the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine , fenugreek ( Trigonella foenum-graecum ) was first mentioned in “an Egyptian papyrus” dating back to 1500 BC This culinary herb has traditionally been used to support milk production in pregnant women, healthy digestion and even to reduce inflammatory conditions relating to the skin . Menurut National Center for Complementary dan Alternatif Medicine, fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) pertama kali disebutkan pada "papirus Mesir" dating kembali ke 1500 SM kuliner ini ramuan secara tradisional telah digunakan untuk mendukung produksi susu pada ibu hamil, sehat pencernaan dan bahkan untuk mengurangi kondisi-kondisi peradangan yang berkaitan dengan kulit. However, in recent years scientists have focused on fenugreek's ability to counter several maladies that are extremely common in the 21st century. Namun, dalam beberapa tahun terakhir para ilmuwan telah difokuskan pada kemampuan fenugreek untuk melawan beberapa penyakit yang sangat umum di abad ke-21. ( 1 ) (1)
Two recent studies on fenugreek indicate that it may play a valuable role in the arena of hunger management . Dua studi baru-baru ini di fenugreek menunjukkan bahwa hal itu mungkin memainkan peran berharga dalam arena kelaparan manajemen. The first trial was published in the November 2009 issue of Phytotherapy Research . Sidang pertama diterbitkan dalam edisi November 2009 Penelitian Phytotherapy. It involved 18 “healthy obese subjects”. Melibatkan 18 "gemuk sehat subjek". Each of the participants ate three breakfasts that were supplemented with varying levels of fenugreek fiber - 0 grams (used as a comparison), 4 grams or 8 grams. Masing-masing peserta makan tiga sarapan yang dilengkapi dengan berbagai tingkat fenugreek serat - 0 gram (digunakan sebagai pembanding), 4 gram atau 8 gram. Dietary records were kept that detailed the food consumed in meals and snacks following the experimental breakfasts. Catatan makanan disimpan rinci makanan yang dikonsumsi dalam makanan dan snack berikut sarapan eksperimental. Several significant findings were noted: Beberapa temuan yang signifikan dicatat:
- The meals containing 8 grams of fenugreek fiber supported feelings of fullness and satiety. Makanan yang mengandung 8 gram serat didukung fenugreek perasaan kenyang dan kenyang.
- This reduced level of hunger decreased subsequent food consumption on the days when the 8 gram dosage was administered. Ini mengurangi rasa lapar menurun tingkat konsumsi makanan berikutnya pada hari-hari ketika dosis 8 gram ini dikelola.
- The caloric intake in the groups receiving 4 and 8 grams of fenugreek also dropped during lunch time meals. Asupan kalori dalam kelompok-kelompok menerima 4 dan 8 gram fenugreek juga menurun selama waktu makan siang makan. ( 2 ) (2)
A study from the October 2009 edition of the European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology explains that fenugreek seeds have been shown to reduce “feeding behavior in animals, but strong clinical data (in humans) are lacking”. Sebuah studi dari edisi Oktober 2009 di European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology menjelaskan bahwa biji fenugreek telah terbukti mengurangi "perilaku makan pada hewan, tetapi kuat data klinis (pada manusia) yang kurang". In order to remedy this information gap, a group of 12 healthy male volunteers were enrolled in a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study. Dalam rangka untuk mengatasi kesenjangan informasi ini, sekelompok laki-laki yang sehat dari 12 relawan yang terdaftar dalam acak buta ganda terkontrol plasebo-. On three separate occasions, the men were given either a placebo, 588 mg of a fenugreek seed extract or 1,176 mg of the extract. Pada tiga kesempatan terpisah, orang-orang baik diberi plasebo, 588 mg ekstrak biji fenugreek atau 1.176 mg ekstrak. There was a “washout period” of 14 days between each test in order to rule out any competing influence. Ada "periode washout" dari 14 hari di antara setiap tes dalam rangka untuk menyingkirkan semua pengaruh bersaing. The results of this experiment indicate that the higher dosage of fenugreek significantly reduced fat and total caloric intake while having no ill effect on nutrient levels. Hasil percobaan ini menunjukkan bahwa dosis yang lebih tinggi secara signifikan mengurangi lemak fenugreek dan total kalori asupan sementara tidak memiliki efek buruk pada tingkat gizi. ( 3 ) (3)
If a reduction in appetite was all that fenugreek could accomplish, I probably wouldn't devote an entire column to it. Jika penurunan nafsu makan itu yang fenugreek bisa menyelesaikan, aku mungkin tidak akan mencurahkan seluruh kolom untuk itu. But it also appears to provide some valuable benefits with regard to blood sugar disorders and cardiovascular health. Tetapi juga muncul untuk memberikan manfaat yang berharga berkaitan dengan gangguan gula darah dan kesehatan jantung. Here are some of the key findings that I discovered while sifting through the most recent scientific data: Berikut adalah beberapa temuan kunci yang saya temukan saat memilah-milah yang paling baru data ilmiah:
- A new Iranian study examined the effects of 10 grams of “powdered fenugreek seeds” in a group of 24 type 2 diabetics. Studi Iran baru meneliti efek dari 10 gram "fenugreek bubuk benih" dalam kelompok dari 24 penderita diabetes tipe 2. The fenugreek powder was either “soaked in hot water” or mixed into yogurt and fed to the diabetics over the course of 8 weeks. Fenugreek bubuk yang baik "direndam dalam air panas" atau dicampur ke dalam yoghurt dan diberi makan kepada penderita diabetes selama 8 minggu. The subjects who were in the “hot water” group demonstrated statistically significant reductions in fasting blood sugar, VLDL (”bad”) cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Subyek yang berada di dalam "air panas" kelompok yang signifikan secara statistik menunjukkan penurunan gula darah puasa, VLDL ( "buruk") kolesterol dan trigliserid. But those receiving the fenugreek-enhanced yogurt showed no such benefits. Tetapi mereka yang menerima yoghurt fenugreek yang disempurnakan tidak menunjukkan manfaat tersebut. This research suggests that certain water soluble fractions of fenugreek may be responsible for its therapeutic activity. Penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa fraksi larut dalam air tertentu dari fenugreek mungkin bertanggung jawab untuk aktivitas terapeutik. ( 4 ) (4)
- Several animal studies provide a basis for the lipid-modifying effects of fenugreek exhibited in the previous study. Beberapa studi hewan menyediakan dasar untuk memodifikasi lipid-efek fenugreek dipamerkan dalam studi sebelumnya. An Indian trial from the October 2009 issue of the journal Obesity , discovered that fenugreek could assist the body in processing LDL cholesterol and decrease fat accumulation in mice. Pengadilan India dari edisi Oktober 2009 jurnal Obesitas, menemukan bahwa fenugreek dapat membantu tubuh dalam memproses kolesterol LDL dan penurunan penimbunan lemak pada tikus. These results may help explain why other recent animal studies demonstrate fenugreek's ability to reduce plaque formation in the arteries of rabbits and even reduce the likelihood of cholesterol-based gallstones in mice receiving a high cholesterol diet. Hasil ini mungkin bisa membantu menjelaskan mengapa hewan lain studi baru-baru ini menunjukkan kemampuan fenugreek untuk mengurangi pembentukan plak di arteri kelinci dan bahkan mengurangi kemungkinan batu empedu kolesterol berbasis pada tikus yang menerima diet kolesterol tinggi. ( 5 , 6 , 7 ) (5, 6, 7)
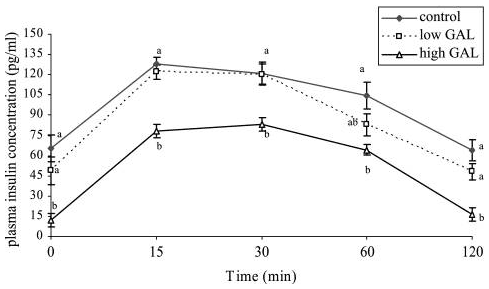
Fenugreek Fiber (Galactomannan) and Blood Sugar Control Fenugreek Fiber (Galactomannan) dan Kontrol Gula Darah
GAL = Galactomannan (Soluble Fiber) GAL = Galactomannan (Soluble Fiber)
Source: J Clin Biochem Nutr. Sumber: J Clin Nutr Biochem. 2008 November; 43(3): 167–174. 2008 November; 43 (3): 167-174. ( a ) (A) Perhaps the biggest question about fenugreek that's currently being examined is how and why it works as well as it does. Mungkin pertanyaan terbesar tentang fenugreek yang saat ini sedang diperiksa adalah bagaimana dan mengapa hal itu bekerja dengan baik seperti halnya. As I write this, there are food scientists fast at work trying to find a way to incorporate fenugreek into our modern food supply. Saat saya menulis ini, ada makanan cepat di tempat kerja ilmuwan berusaha mencari cara untuk menggabungkan fenugreek ke suplai makanan modern kita. An October 2009 study in the Journal of Medicinal Food tested the use of a proprietary fenugreek flour which was added to a commercial bread mix. Oktober 2009 Sebuah studi dalam Journal of Medicinal Food menguji penggunaan fenugreek berpemilik tepung yang ditambahkan ke campuran roti komersial. The experimental bread contained 5% fenugreek flour. Roti eksperimental berisi 5% fenugreek tepung. Testing on 8 “diet-controlled diabetic subjects” found that the fenugreek bread helped to manage blood sugar and insulin more successfully than a 100% whole wheat bread. Pengujian pada 8 "diet diabetes dikendalikan subjek" menemukan bahwa roti fenugreek membantu untuk mengelola gula darah dan insulin lebih berhasil dari 100% gandum roti. Another important finding was that the taste of the fenugreek bread was “indistinguishable from the whole wheat bread control”. Temuan penting lainnya adalah bahwa rasa dari roti fenugreek "dibedakan dari roti gandum kontrol". ( 8 ) (8)
Very few health conditions are brought about by genetic factors alone. Some people may be prone to elevated cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity or type 2 diabetes. But it’s extremely uncommon that such health concerns are solely influenced by a familial predisposition. More often than not these conditions are influenced by diet and lifestyle choices that are less than optimal. A pertinent analogy for this might be that genes are like a field. If you eat well, exercise regularly, practice stress reduction and supplement wisely, you will, in effect, encourage lush green plant life to grow. However, if you don’t take proper care of yourself, the field will become dry and lifeless. When ash or a spark comes drifting your way, which type of a field would you rather be?

On many occasions I’ve emphasized that supplements are not a replacement for healthy lifestyle choices. But the fact of the matter is that many people fall short of their dietary and exercise goals. Another reality is that some people have stronger genetic hurdles to overcome. In both of these instances, supplements can often play a more prominent role in managing wellness naturally.
According to the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine, fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) was first mentioned in “an Egyptian papyrus” dating back to 1500 B.C. This culinary herb has traditionally been used to support milk production in pregnant women, healthy digestion and even to reduce inflammatory conditions relating to the skin. However, in recent years scientists have focused on fenugreek’s ability to counter several maladies that are extremely common in the 21st century. (1)
Two recent studies on fenugreek indicate that it may play a valuable role in the arena of hunger management. The first trial was published in the November 2009 issue of Phytotherapy Research. It involved 18 “healthy obese subjects”. Each of the participants ate three breakfasts that were supplemented with varying levels of fenugreek fiber - 0 grams (used as a comparison), 4 grams or 8 grams. Dietary records were kept that detailed the food consumed in meals and snacks following the experimental breakfasts. Several significant findings were noted:
- The meals containing 8 grams of fenugreek fiber supported feelings of fullness and satiety.
- This reduced level of hunger decreased subsequent food consumption on the days when the 8 gram dosage was administered.
- The caloric intake in the groups receiving 4 and 8 grams of fenugreek also dropped during lunch time meals. (2)
A study from the October 2009 edition of the European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology explains that fenugreek seeds have been shown to reduce “feeding behavior in animals, but strong clinical data (in humans) are lacking”. In order to remedy this information gap, a group of 12 healthy male volunteers were enrolled in a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study. On three separate occasions, the men were given either a placebo, 588 mg of a fenugreek seed extract or 1,176 mg of the extract. There was a “washout period” of 14 days between each test in order to rule out any competing influence. The results of this experiment indicate that the higher dosage of fenugreek significantly reduced fat and total caloric intake while having no ill effect on nutrient levels. (3)
If a reduction in appetite was all that fenugreek could accomplish, I probably wouldn’t devote an entire column to it. But it also appears to provide some valuable benefits with regard to blood sugar disorders and cardiovascular health. Here are some of the key findings that I discovered while sifting through the most recent scientific data:
- A new Iranian study examined the effects of 10 grams of “powdered fenugreek seeds” in a group of 24 type 2 diabetics. The fenugreek powder was either “soaked in hot water” or mixed into yogurt and fed to the diabetics over the course of 8 weeks. The subjects who were in the “hot water” group demonstrated statistically significant reductions in fasting blood sugar, VLDL (”bad”) cholesterol and triglyceride levels. But those receiving the fenugreek-enhanced yogurt showed no such benefits. This research suggests that certain water soluble fractions of fenugreek may be responsible for its therapeutic activity. (4)
- Several animal studies provide a basis for the lipid-modifying effects of fenugreek exhibited in the previous study. An Indian trial from the October 2009 issue of the journal Obesity, discovered that fenugreek could assist the body in processing LDL cholesterol and decrease fat accumulation in mice. These results may help explain why other recent animal studies demonstrate fenugreek’s ability to reduce plaque formation in the arteries of rabbits and even reduce the likelihood of cholesterol-based gallstones in mice receiving a high cholesterol diet. (5,6,7)
Fenugreek Fiber (Galactomannan) and Blood Sugar Control
GAL = Galactomannan (Soluble Fiber)
Source: J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2008 November; 43(3): 167–174. (
a)
Perhaps the biggest question about fenugreek that’s currently being examined is how and why it works as well as it does. As I write this, there are food scientists fast at work trying to find a way to incorporate fenugreek into our modern food supply. An October 2009 study in the Journal of Medicinal Food tested the use of a proprietary fenugreek flour which was added to a commercial bread mix. The experimental bread contained 5% fenugreek flour. Testing on 8 “diet-controlled diabetic subjects” found that the fenugreek bread helped to manage blood sugar and insulin more successfully than a 100% whole wheat bread. Another important finding was that the taste of the fenugreek bread was “indistinguishable from the whole wheat bread control”. (8)
A substance by the name of 4-hydroxyisoleucine is believed to be at least partially responsible for the blood sugar balancing effect of fenugreek. This “atypical branched-chain amino acid” has been shown to reduce insulin resistance in the liver and muscles, and stimulate insulin secretion by the pancreas. The weight loss demonstrated in certain animal studies is postulated as being one more way in which fenugreek can cause a decline in blood sugar and plasma insulin concentrations. This evidence recently prompted a group of Canadian researchers to remark that, “4-hydroxyisoleucine, a simple, plant-derived amino acid, may represent an attractive new candidate for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, obesity and dyslipidemia, all key components of metabolic syndrome”. Other scientists report that even long term exposure (in animal models) to 4-hydroxyisoleucine does not damage the liver and appears to improve certain cardiovascular risk factors such as HDL (”good”) cholesterol levels. (9,10,11)
The truth of the matter is that researchers are often left wondering exactly how natural “medicines” work. Herbal extracts are frequently comprised of hundreds, if not thousands, of naturally-occurring chemicals. Most prescription medications are synthesized in a laboratory and contain only one, isolated chemical. This is partially why it’s not yet clear whether the healing properties of fenugreek are due solely to 4-hydroxyisoleucine, water soluble phytochemicals or possibly even a viscous form of fiber known as galactomannan. The overall potential of fenugreek is also not entirely clear. Preliminary research indicates that it may benefit aspects of health that extend far beyond blood sugar, cholesterol and weight. In recent years, scientific trials point to fenugreek as a possible analgesic (pain reliever), a liver protector and a memory enhancer. There is even a study underway to verify its time tested ability to safely support lactation in women who have difficulty producing adequate breast milk. Fenugreek has indeed come full circle. But now, that circle is expanding. We’re learning more about this valuable spice each day and the information is becoming available just in the nick of time. (12,13,14,15,16,17)